This is a simple step-by-step guide to installing Microsoft's newest version of SQL Server with Reporting Services in stand-alone mode (the alternative is SharePoint Integrated, I'll deal with all the steps necessary to do that installation separately in a few days/weeks time).
The first step is to install your Windows 2008R2 box and get it fully upgraded to the latest patch levels (SP1). Then you can run the setup.exe on the installation DVD;
 |
| SQL Server 2012: Installation Centre |
Select
"Installation" from the list of options on the left;
 |
| SQL Server 2012: Installation Options |
Select
"New SQL Server stand-alone installation ..." which is the top option on the right. After a few seconds wait (but I guess that probably depends on the speed and power of your system!) the following dialog appears;
 |
| SQL Server 2012: Setup Support Rules |
The installation program has checked your system and, on the system I'm using, found nothing that prevents the installation from proceeding. If you are interested in seeing the "Detailed Report". Once you've got a good set of passes click
"OK". A "please wait" dialog will appear and after a few seconds the next dialog;
 |
| SQL Server 2012: Product Key |
You now need to enter your Product Key. If you are using the MSDN edition then it will be pre-populated, if you don't have one when you can just select one of the "Free" editions. Once you've entered the details click
"Next";
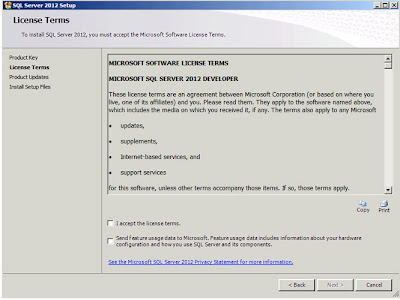 |
| SQL Server 2012: License Terms |
No installation process would be complete without a 20-page Licensing Agreement and this one is no different. After you've read the entire document (you do do that right? *cough*) click on the "I accept the license terms". I also select the "Send feature usage data to Microsoft" and if you don't you'll only have yourself to blame when the features I use and tell them about are prioritised for improvement and the features you use but keep secret about aren't ... ;-) Click
"Next";
 |
| SQL Server: Install Setup Files |
This dialog will only appear for a few seconds, as soon as the installation files have been successfully installed you are presented with the next dialog;
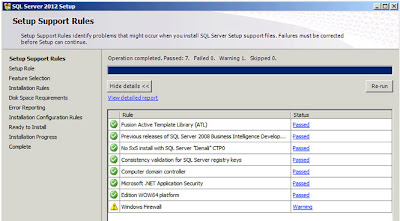 |
| SQL Server: Setup Support Rules |
Again I've made the Detailed Report for this check available via Google Docs here. As you'll see there is one Warning related to the
"Windows Firewall", I'm going to ignore this and just move on. Click
"Next";
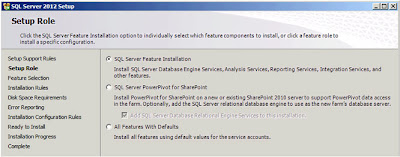 |
| SQL Server: Setup Role |
The default option,
"SQL Server Feature Installation" is the one I'm after so I'll just click "Next";
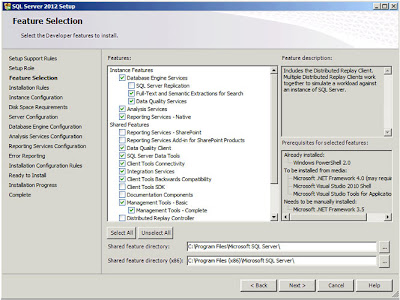 |
| SQL Server: Feature Selection |
And this is the part where things start to get complicated. What exactly do you want your SQL Server to be doing? I'm going to install pretty much everything except the SharePoint integrated features (the first two shared features; Reporting Services - SharePoint, and Reporting Services Add-in for SharePoint Products). Click
"Next";
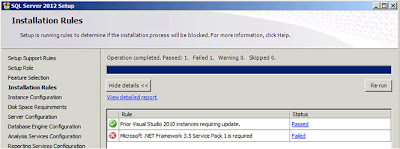 |
| SQL Server: Installation Rules |
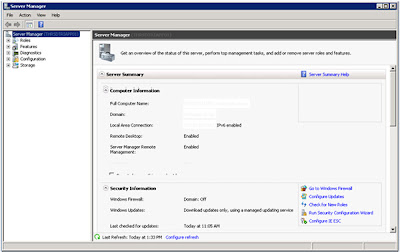
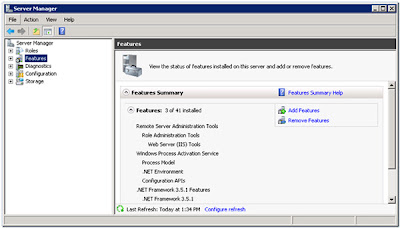
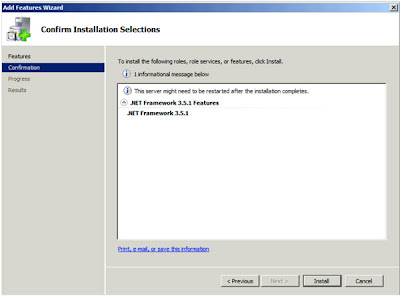
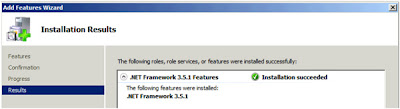
So we now have another check, the third, to make sure the system is capable of running the options I've selected. And now it
"Failed" as "Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5 Service Pack 1 is required". The instructions for enabling this feature I have also blogged about, click here. When I did this no-reboot was required. After you've enabled the feature click on
"Re-run" in the dialog;
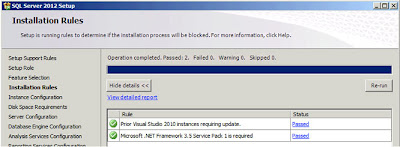 |
| SQL Server: Installation Rules (Attempt 2) |
As you can see the check that had previously failed has now passed. The Detailed log is available (via Google Docs) here. Click
"Next";
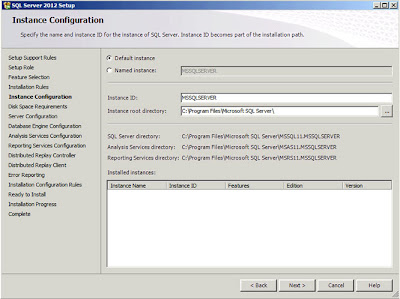 |
| SQL Server: Instance Configuration |
There isn't anything here I need to change so just click
"Next". There will be a brief pause while the installation program checks to see if sufficient disk space exists to install the options you have selected. After a few seconds a report will be displayed;
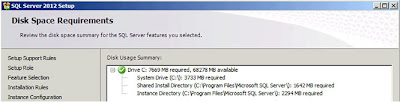 |
| SQL Server: Disk Space Requirements |
Click
"Next";
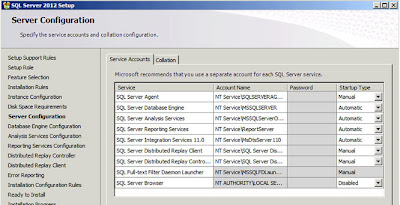 |
| SQL Server: Server Configuration |
It's pretty unlikely that you'll want to change anything here (all these are services you can always change later). The one thing you might want to check if you are deploying to non-English customers is that the correct options are selected under the "Collation" tab - this is especially true if your system will be used to store multi-byte data such as Chinese, Japanese, Korean, etc. characters. Click
"Next" when you're done;
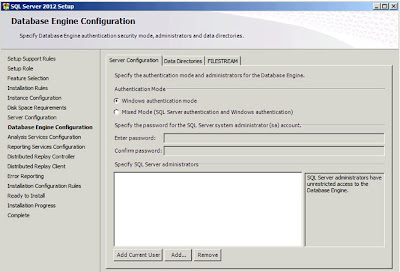 |
| SQL Server: Database Engine Configuration |
I always use "Windows authentication". I usually add in a few AD groups representing the entire company (we are an IT Service company) on the basis that I never know who I might want to share it with. This is your chance to secure the system either as tightly or loosely as you wish. Click
"Next";
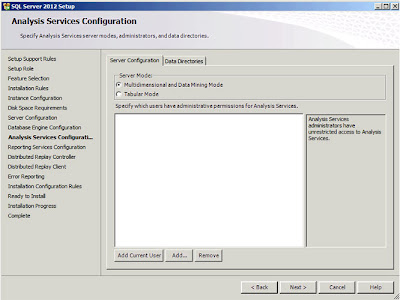 |
| SQL Server: Analysis Services Configuration |
And the same again really. You need to enter the users who will have access to the Analysis Services. Once you're happy with this click
"Next";
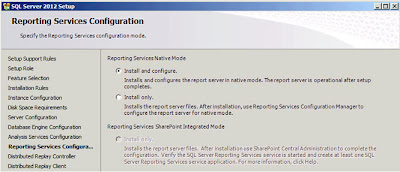 |
| SQL Server: Reporting Services Configuration |
The default option,
"Install and Configure", is the option I'm interested in so just click
"Next";
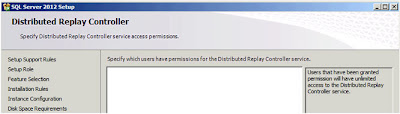 |
| SQL Server: Distributed Replay Controller |
Whilst appearing to be exactly the same as other
"Pick the users" dialog box this one is subtly (invisibly!) different; you cannot select groups. If you try when you click "Next" you get an error;
The specified account 'XX\YYYY' for setting 'CTLRUSERS' is a group account. You can only use a user account. Add in the users for this feature and click
"Next";
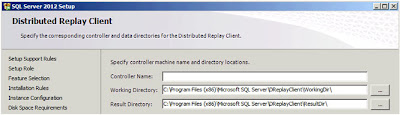 |
| SQL Server: Distributed Replay Chat |
Enter the name of your controller (or leave blank) and then click
"Next";
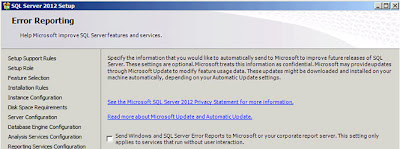 |
| SQL Server: Error Reporting |
I always check this check box (to send error reports to Microsoft) so that errors I encountered will hopefully be dealt with in future releases! Click
"Next" when you're done and another round of checks will be executed and after a few seconds you will be presented with a report;
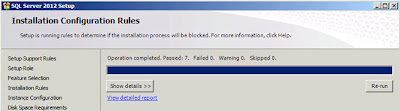 |
| SQL Server: Installation Configuration Rules |
Click
"Next";
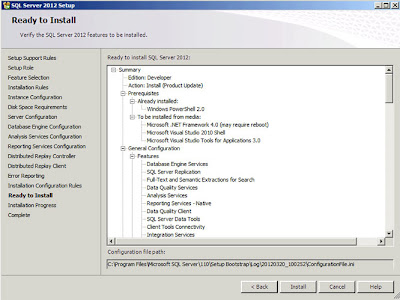 |
| SQL Server: Ready To Install |
Click
"Install" to begin the install process. The installation itself on the development system I was using took around 25/30 minutes. After the install is complete you will see the following dialog;
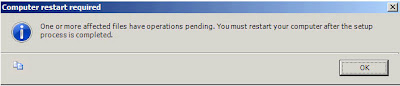 |
| SQL Server: Computer Restart Required |
Click
"OK" and under this is the final installation report;
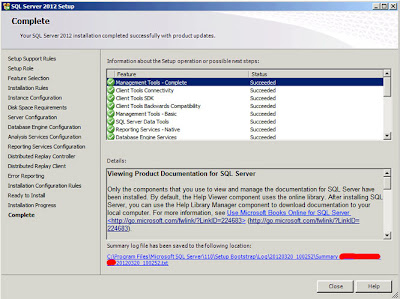 |
| SQL Server: Complete (Install Report) |
A restart is required, after the restart running Internet Explorer and pointing to the the SQL Server Reporting Services URL will (after logging in) take you to the standard webpage.